public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
double r = 4.5;
double u = Math.PI * r;
System.out.println(
"The circumference of a circle with radius " + r + " is " + u);
}
}
The result was -727379968 due to an int overflow.
The result is -1.1102230246251565E-16 , because 0.1 cannot be represented exactly in the binary system. A test program is approximately...
System.out.println(0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1+0.1-1.0);
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
double e = Math.exp(1.0);
int n = 10;
double r = Math.pow(1 + 1.0 / n, n);
System.out.println(r + ", " + (e - r));
n = 100;
r = Math.pow(1 + 1.0 / n, n);
System.out.println(r + ", " + (e - r));
n = 1000;
r = Math.pow(1 + 1.0 / n, n);
System.out.println(r + ", " + (e - r));
n = 10000;
r = Math.pow(1 + 1.0 / n, n);
System.out.println(r + ", " + (e - r));
}
}
The output is
2.5937424601000023, 0.12453936835904278 2.7048138294215285, 0.01346799903751661 2.7169239322355936, 0.0013578962234515046 2.7181459268249255, 1.35901634119584E-4
Note that n=1000 is sufficient .
System.out.println((char)27);
(x>=1) && (x<=2)
The result is NaN (Not a Number).
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
double sum=0;
for (int i=1; i<100; i++) sum+=i*i;
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=27;
while (n!=1)
{
System.out.println(n);
if (n%2==0) n=n/2;
else n=3*n+1;
}
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int a=1,b=1;
for (int i=3; i<=20; i++)
{
int c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
a=b; b=c;
}
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
double x=0;
while (true)
{
System.out.println(x);
x=Math.cos(x);
}
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
double x=0,old=x;
do
{
System.out.println(x);
old=x;
x=Math.cos(x);
}
while (Math.abs(x-old)>1e-13);
}
}
What value does this converge towards?
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
int n = 10000; // Number of random numbers
double R[] = new double[n]; // creates space for n numbers
// Random numbers:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
R[i] = Math.random();
// generate random numbers
// Average:
double sum = 0;
for (double x : R)
sum += x; // calculate sum
double mean = sum / n;
System.out.println("Average : " + mean);
// Sample deviation:
sum = 0;
for (double x : R)
sum += (mean - x) * (mean - x);
// Calculate variance
System.out.println("Standard deviation: "
+ Math.sqrt(sum / (n - 1)));
// Distribution:
int m = 10;
int I[] = new int[m]; // Platz fuer m Zaehler
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
I[i] = 0; // initialize with 0
for (double x : R) // zaehlen
{
int j = (int) Math.floor(x * m);
// In which interval does R[i] lie?
if (j >= m)
j = m - 1; // falls R[i]==1.0
I[j]++; // erhoehe Zaehler
}
// Edition:
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) // Output of the counts
System.out.println((j + 1) + " : " + I[j]);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=1000;
double R[]=new double[n];
int i;
for (i=0; i<n; i++) R[i]=Math.random();
double max=R[0];
for (i=1; i<n; i++)
if (R[i]>max) max=R[i];
System.out.println(max);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int i,n=1000;
double max=Math.random();
for (i=1; i<n; i++)
{
double h=Math.random();
if (h>max) max=h;
}
System.out.println(max);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int i, n = 1000;
double R[] = new double[1000];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
R[i] = Math.random();
double max1, max2;
if (R[0] > R[1])
{
max1 = R[0];
max2 = R[1];
} else
{
max2 = R[0];
max1 = R[1];
}
for (i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
if (R[i] > max1)
{
max2 = max1;
max1 = R[i];
} else if (R[i] > max2)
max2 = R[i];
}
System.out.println(max1);
System.out.println(max2);
}
}
In this task, you must be careful to calculate from back to front, otherwise the information still needed will be overwritten.
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=20;
int p[]=new int[n];
p[0]=1;
int i,j;
for (i=1; i<n; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<i; j++) System.out.print(p[j]+" ");
System.out.println();
p[i]=1;
for (j=i-1; j>=1; j--) p[j]=p[j]+p[j-1];
p[0]=1;
}
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int i,n=100;
double y[]=new double[n+1];
for (i=0; i<=n; i++) y[i]=Math.cos(i*0.01);
double sum=0;
for (i=0; i<=n; i++) sum+=y[i];
System.out.println(sum*0.01);
sum=y[0]+4*y[1]+y[n];
for (i=2; i<n; i+=2) sum+=2*y[i]+4*y[i+1];
System.out.println(sum*0.01/3);
System.out.println(Math.sin(1));
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(cosh(1.5));
}
static double sinh (double x)
{
return (Math.exp(x) - Math.exp(-x)) / 2;
}
static double cosh (double x)
{
return (Math.exp(x) + Math.exp(-x)) / 2;
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
double R[] = new double[1000];
for (int i = 0; i < R.length; i++)
R[i] = Math.random();
System.out.println(max(R));
}
static double max (double x[])
{
double m = x[0];
for (int i = 1; i < x.length; i++)
if (m < x[1])
m = x[1];
return m;
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println((int) choose(49, 6));
}
static double fak (int n)
{
double r = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
r *= i;
return r;
}
static double choose (int n, int k)
{
return fact(n) / (fact(k) * fact(n - k));
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println((int) choose(49, 6));
}
static double choose (int n, int k)
{
if (k > n / 2)
k = n - k;
double r = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
r *= (n - i + 1) / (double) i;
return r;
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(pow(2, 10));
}
static double pow (double x, int n)
{
if (n == 0)
return 1;
else if (n % 2 == 0)
return sqr(pow(x, n / 2));
else
return x * sqr(pow(x, n / 2));
}
static double sqr (double x)
{
return x * x;
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(ggt(52, 273));
}
static int ggt (int n, int m)
{
if (m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
else
{
int r = n % m;
if (r != 0)
return ggt(m, r);
else
return m;
}
}
}
class Cord
{
private double X, Y;
public Koord (double x, double y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
public double x ()
{
return X;
}
public double y ()
{
return Y;
}
public void set (double x, double y)
{
X = x;
Y = y;
}
}
class Point extends String
{
public Punkt (double x, double y)
{
super(x, y);
}
}
class Circle extends Chord
{
private double R;
public Kreis (double x, double y, double r)
{
super(x, y);
R = r;
}
double r ()
{
return R;
}
void set (double x, double y, double r)
{
super.set(x, y);
R = r;
}
}
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
Circle k = new Circle(0.5, 0.5, 0.5);
int count = 0, n = 1000000;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
Point p = new Point(Math.random(), Math.random());
if (contains(k, p))
count++;
}
System.out.println((double) count / n);
System.out.println(Math.PI / 4);
}
static boolean contains (Kreis k, Punkt p)
{
if (Math.sqrt(sqr(k.x() - p.x()) + sqr(k.y() - p.y())) < k.r())
return true;
else
return false;
}
static double sqr (double x)
{
return x * x;
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=1000000;
BitSet b=new BitSet(n+1);
int i,j;
for (i=0; i<=n; i++) b.set(i);
for (i=2; i<n; i++)
{
if (b.get(i))
for (j=2*i; j<=n; j+=i) b.clear(j);
}
int count=0;
for (i=2; i<n; i++)
if (b.get(i)) count++;
System.out.println(count);
}
}
import java.util.BitSet;
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=1000000;
BitSet b=new BitSet(n/2);
int i,j,k;
for (k=0; k<=n/2; k++) b.set(k);
double max=Math.sqrt(n);
for (k=0,i=3; i<n && k<max; i+=2,k++)
{
if (b.get(k))
for (j=k+i; j<n/2; j+=i) b.clear(j);
}
int count=0;
for (k=0; k<n/2; k++)
if (b.get(k)) count++;
System.out.println(count+1);
}
}
Note that bit k now represents the number 2k+1 .
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(isPalindrom(args[0]));
}
public static boolean isPalindrom (String s)
{
int i = 0, n = s.length() - 1;
while (i < n)
{
if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(n))
return false;
i++;
n--;
}
return true;
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
System.out.println(simplify(args[0]));
}
public static String simplify (String s)
{
StringBuffer b = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
char c = s.charAt(i);
b.append(c);
while (i < s.length() - 1 && c == s.charAt(i + 1))
i++;
}
return b.toString();
}
}
import java.util.*;
public class Test
{
static public void main (String args[])
{
int n = 1000;
// Setting up an array:
ArrayList<Double> L = new ArrayList<Double>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
L.add(Math.random());
// Calculate average:
double sum = 0;
for (Double x : L)
sum += x.doubleValue();
System.out.println(sum / n);
// Remove all x<0.5:
Iterator<Double> x = L.iterator();
while (x.hasNext())
{
if (x.next().doubleValue() < 0.5)
x.remove();
}
// Output size:
System.out.println(L.size());
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
int n=1000;
LinkedList<Double> L=new LinkedList<Double>();
for (int i=0; i<1000; i++) L.add(Math.random());
// Automatic conversion!
ArrayList<Double> A=new ArrayList<Double>();
A.addAll(L);
System.out.println(A.size());
}
}
import java.awt.BasicStroke;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class SinCosCanvas extends Canvas
{
private int width, height;
public double xmin = -10, ymein = -2, xmax = 10, ymax = 2;
// The plot coordinates in the mathematical plane
@Override
public void paint (Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g;
// Anti-alias the graphics context
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_ON);
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(3));
Dimension d = getSize();
width = d.width;
height = d.height;
// Draw:
int c1 = col(xmin), r1 = row(f(xmin)), c2, r2;
// c1,c2 are the old coordinates
// (i.e., the starting points of the lines)
for (int i = 0; i < width; i += 10)
{
double x = xmin + (xmax - xmin) / width * i;
double y = f(x);
c2 = col(x);
r2 = row(y);
g2.drawLine(c1, r1, c2, r2);
c1 = c2;
r1 = r2;
}
}
// The function being plotted:
double f (double x)
{
if (Math.abs(x) < 1e-10)
return 1.0;
else
return Math.sin(x) / x;
}
// Conversion of x-coordinate to screen column
private int col (double x)
{
return (int) ((x - xmin) / (xmax - xmin) * width);
}
// Conversion of y-coordinate to screen line
private int row (double y)
{
return (int) ((ymax - y) / (ymax - ymein) * height);
// Note the inverse of this coordinate
}
}
class SinCosTestFrame extends JFrame
{
public SinCosTestFrame ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new SinCosCanvas());
}
}
public class SinCosPlot
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
JFrame F = new SinCosTestFrame();
F.setSize(600, 600);
F.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
F.setVisible(true);
}
}
import java.awt.*;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
public void paint (Graphics g)
{
Dimension d = getSize();
int w = d.width, h = d.height;
Color C;
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
float x = (float) i / w;
C = new Color(x, x, x);
g.setColor(C);
g.drawLine(i, 0, i, h - 1);
}
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
Frame F = new Frame();
F.setSize(300, 300);
F.add(new TestCanvas());
F.setVisible(true);
}
}
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
@Override
public void paint (Graphics g)
{
Dimension d = getSize();
int w = d.width, h = d.height;
g.drawLine(0, 0, w - 1, h - 1);
g.drawLine(0, h - 1, w - 1, 0);
g.drawRect(0, 0, w - 1, h - 1);
}
@Override
public Dimension getPreferredSize ()
{
return new Dimension(20, 20);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
JFrame F = new JFrame();
F.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
F.setSize(300, 300);
F.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
F.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
F.add("North", new TestCanvas());
F.add("East", new TestCanvas());
F.add("West", new TestCanvas());
F.add("South", new TestCanvas());
F.add("Center", new TestCanvas());
F.setVisible(true);
}
}
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* IntArray contains an array of int with unspecified length.
*/
class IntArray implements Comparable<IntArray>
{
// content
public int[] v;
/**
* Create an IntArray with this size
*
* @param size
*/
public IntArray (int size)
{
v = new int[size];
}
/**
* Format like: "5 6 4 3 2 "
*/
@Override
public String toString ()
{
String s = "";
for (int i : v)
s = s + i + " ";
return s;
}
// Static random for the makeRandom function
static Random random = new Random();
/**
* Create a random IntArray
*
* @param max
* @param maxsize
* @return
*/
public static IntArray makeRandom (int max, int maxsize)
{
// size between 1 and maxsize
int size = random.nextInt(maxsize) + 1;
IntArray intarray = new IntArray(size);
// set random elements
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
intarray.v[i] = random.nextInt(max);
return intarray;
}
/**
* Compare this IntArray to an other, alphabetically. If they are equal up
* to the shorter one, the longer one is greater.
*
* @param other
* @return -1 if this one is smaller, 0 if equal, 1 if this one is larger
*/
@Override
public int compareTo (IntArray other)
{
// Compare all elements of v up to the length of the other
for (int i = 0; i < v.length; i++)
{
// equal, but the this one is longer
if (i >= other.v.length)
return 1;
// one element of this one is smaller
if (v[i] < other.v[i])
return -1;
// one element of this one is bigger
if (v[i] > other.v[i])
return 1;
}
// equal, but the other is onger
if (v.length < other.v.length)
return -1;
// equal and equal size
return 0;
}
}
public class IntArraySortTest
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
// create a Vector for IntArrays
Vector<IntArray> test = new Vector<IntArray>();
// create 20 random ones
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
test.add(IntArray.makeRandom(5, 5));
// sort
Collections.sort(test);
// print all
for (IntArray v : test)
System.out.println(v);
}
}
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.Frame;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas implements MouseListener
{
private int x = -100, y = -100;
public TestCanvas ()
{
addMouseListener(this);
}
@Override
public void paint (Graphics g)
{
g.drawRect(x - 10, y - 10, 20, 20);
}
@Override
public void mousePressed (MouseEvent e)
{
x = e.getX();
y = e.getY();
repaint();
}
@Override
public void mouseReleased (MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public void mouseEntered (MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public void mouseExited (MouseEvent e)
{
}
@Override
public void mouseClicked (MouseEvent e)
{
}
}
class TestFrame extends Frame
{
public TestFrame ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
add(new TestCanvas());
setVisible(true);
addWindowListener(
new WindowAdapter()
{
@Override
public void windowClosing (WindowEvent e)
{
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
new TestFrame();
}
}
or with a mouse adapter
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
private int x = -100, y = -100;
public TestCanvas ()
{
addMouseListener(
new MouseAdapter()
{
@Override
public void mousePressed (MouseEvent e)
{
x = e.getX();
y = e.getY();
repaint();
}
});
}
@Override
public void paint (Graphics g)
{
g.drawRect(x - 10, y - 10, 20, 20);
}
}
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class TestFrame extends JFrame
{
public TestFrame ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
if (e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ESCAPE)
{
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
}
});
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
new TestFrame();
}
}
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
public TestCanvas ()
{
addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Canvas: " + e);
}
});
}
}
class TestFrame extends JFrame
{
public TestFrame ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
add(new TestCanvas());
setVisible(true);
addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Frame: " + e);
}
});
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
new TestFrame();
}
}
Initially, events are sent to the window. After clicking inside the window, the canvas always receives focus. If two canvases are placed in the frame, focus remains on the first one.
To ensure the frame receives keyboard events, simply register the window as a key listener for the canvas. To give the canvas immediate focus, use the `requestFocus()` method .
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
}
class TestFrame extends JFrame
{
public TestFrame ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
TestCanvas canvas = new TestCanvas();
add(canvas);
setVisible(true);
canvas.addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Frame: " + e);
}
});
canvas.requestFocus();
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
new TestFrame();
}
}
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class Test extends JFrame
{
public Test ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
Canvas canvas;
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", canvas = new Canvas());
add("South", new TextField());
setVisible(true);
canvas.addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
new Test();
}
}
The answer is: No.
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.TextField;
import java.awt.event.KeyAdapter;
import java.awt.event.KeyEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
class TestCanvas extends Canvas
{
public TestCanvas ()
{
addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
System.out.println("Canvas :" + e);
}
});
addMouseListener(
new MouseAdapter()
{
@Override
public void mousePressed (MouseEvent e)
{
requestFocus();
}
});
}
}
class Test extends JFrame
{
public Test ()
{
super("Test Frame");
setSize(300, 300);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
TestCanvas canvas;
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", canvas = new TestCanvas());
add("South", new TextField());
setVisible(true);
canvas.addKeyListener(
new KeyAdapter()
{
@Override
public void keyPressed (KeyEvent e)
{
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
new Test();
}
}
The answer is: Yes.
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Canvas;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.event.ItemEvent;
import java.awt.event.ItemListener;
import java.awt.event.MouseAdapter;
import java.awt.event.MouseEvent;
import java.awt.event.MouseMotionAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import javax.swing.JComboBox;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
class PaintCanvas extends Canvas
{
Color C;
int X, Y;
public PaintCanvas ()
{
// Starts dragging if the button is down inside the canvas.
addMouseListener(
new MouseAdapter()
{
@Override
public void mousePressed (MouseEvent e)
{
X = e.getX();
Y = e.getY();
}
});
// Allows to follow dragging of the mouse.
addMouseMotionListener(
new MouseMotionAdapter()
{
@Override
public void mouseDragged (MouseEvent e)
{
Graphics g = getGraphics();
g.setColor(C);
g.drawLine(X, Y, e.getX(), e.getY());
X = e.getX();
Y = e.getY();
g.dispose();
}
});
setBackground(Color.black);
}
public void setColor (Color c)
{
C = c;
}
}
class TestFrame extends JFrame
implements ItemListener
{
String strings[] =
{ "white", "blue", "red", "green", "yellow", "pink" };
Color colors[] =
{ Color.white, Color.blue, Color.red, Color.green,
Color.yellow, Color.pink };
JComboBox<String> choice;
PaintCanvas canvas;
public TestFrame ()
{
super("Test");
setLayout(new BorderLayout());
add("Center", canvas = new PaintCanvas());
canvas.setColor(colors[0]);
JPanel center = new JPanel();
center.add(choice = new JComboBox<String>());
for (int i = 0; i < strings.length; i++)
choice.addItem(strings[i]);
choice.addItemListener(this);
choice.setSelectedItem(strings[0]);
add("South", center);
addWindowListener(
new WindowAdapter()
{
@Override
public void windowClosing (WindowEvent e)
{
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
setSize(600, 600);
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setVisible(true);
}
@Override
public void itemStateChanged (ItemEvent e)
{
int i = choice.getSelectedIndex();
if (i >= 0)
canvas.setColor(colors[i]);
}
}
public class Test
{
public static void main (String args[])
{
new TestFrame();
}
}

import java.awt.BasicStroke;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
/**
* A thread that becomes active every 1000 ms.
*/
class RedrawThread extends Thread
{
JPanel canvas;
boolean stop = false;
public RedrawThread (JPanel canvas)
{
this.canvas = canvas;
start();
}
@Override
public void run ()
{
while (!stop)
{
Try // Necessary!
{
sleep(1000); // Wait 1 second
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
canvas.repaint();
}
}
}
class Display extends JPanel
{
int w, h;
public Display ()
{
setPreferredSize(new Dimension(300, 300));
// Set panel to Double Buffered
setDoubleBuffered(true);
}
@Override
public void paint (Graphics graphics)
{
Graphics2D g = (Graphics2D) graphics;
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
// Due to double buffering, we have to delete manually.
w = getWidth();
h = getHeight();
g.clearRect(0, 0, w, h);
g.setColor(Color.gray.brighter());
g.fillOval(0, 0, w - 1, h - 1);
Date date = new Date();
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.setTime(date);
int hour = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
int minute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
int second = calendar.get(Calendar.SECOND);
hand(g, (hour / 12.0 + minute / 720.0), 0.6,
Color.blue.darker(), 4);
hand(g, minute / 60.0, 0.8, Color.blue.darker(), 3);
hand(g, second / 60.0, 0.75, Color.green.darker(), 2);
}
public void hand (Graphics2D g, double w, double l, Color c, int width)
{
g.setColor(c);
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(width));
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
w = Math.PI / 2 - 2 * w * Math.PI;
x1 = -Math.cos(w) * 0.1;
y1 = -Math.sin(w) * 0.1;
x2 = Math.cos(w) * l;
y2 = Math.sin(w) * l;
g.drawLine(col(x1), row(y1), col(x2), row(y2));
}
public int col (double x)
{
return (int) (x * w / 2 + w / 2);
}
public int row (double y)
{
return h - (int) (y * h / 2 + h / 2);
}
}
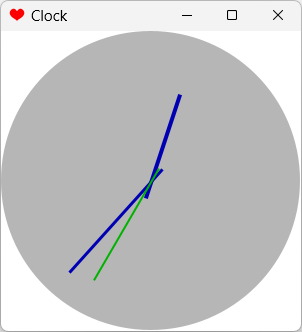
public class Test extends JFrame
{
RedrawThread redraw;
public Test ()
{
super("Clock");
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setIconImage(new javax.swing.ImageIcon(
getClass().getResource("hearts32.png")).getImage());
Display display = new Display();
add("Center", display);
redraw = new RedrawThread(display);
addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()
{
@Override
public void windowClosing (WindowEvent e)
{
redraw.stop = true;
}
});
pack();
setLocationRelativeTo(null);
setVisible(true);
}
public static void main (String args[])
{
new Test();
}
}